which of the following would the nurse expect to find in a client with severe hyperthyroidism?
 Pharmacology Review Flashcards | Quizlet
Pharmacology Review Flashcards | QuizletDo not delay your attention in Mayo ClinicRemarked conditions DiagnosisHyrothyroidism is diagnosed by: Blood tests. Blood tests that measure thyroxine and thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) can confirm the diagnosis. High levels of thyroxine and low or non-existent amounts of TSH indicate a hyperactive thyroid. The amount of TSH is important because it is the hormone that indicates your thyroid gland to produce more thyroxine. These tests are especially necessary for older adults, who may not have classic symptoms of hyperthyroidism. Thyroid blood tests can give false results if you are taking biotin, a vitamin B supplement that can also be found in multivitamins. Tell your doctor if you are using biotin or multivitamin with biotin. To ensure accurate examination, stop taking biotin at least 12 hours before taking the blood. If blood tests indicate hyperthyroidism, your doctor may recommend one of the following tests to help determine why your thyroid is overactive: Radiiodine absorption test. For this test, you take a small dose of radioactive iodine (radioiod) to see how much it will be collected in your thyroid gland. You will be checked after four, six or 24 hours — and sometimes after three periods of time — to see how much I iodine your thyroid has absorbed. A high absorption of radioiodine indicates that the thyroid gland is producing too much thyroxine. The most likely cause is Graves disease or hyperfunctioning thyroid nodules. If you have hyperthyroidism and your radioiode absorption is low, this indicates that the thyroxine stored in the gland is filtering into the bloodstream, which can mean that it has thyroiditis. TreatmentTotal treatments for hyperthyroidism exist. The best approach for you depends on your age, physical condition, the underlying cause of hyperthyroidism, personal preference and the severity of your disorder. Possible treatments include: radioactive iodine. Taken by mouth, the radioactive iodine is absorbed by the thyroid gland, where it causes the gland to contract. Symptoms usually disappear in several months. The excess radioactive iodine disappears from the body in weeks to months. This treatment may cause thyroid activity to be slow enough to be considered subactive (hypothyroidism), and may eventually need to take medication every day to replace thyroxine. Antithyroid drugs. These drugs gradually reduce the symptoms of hyperthyroidism by preventing the thyroid gland from producing excessive amounts of hormones. They include methimazol (Tapazole) and propylithiouracil. Symptoms usually begin to improve within several weeks to months, but treatment with antithyroid drugs usually continues at least one year and often more. For some people, this permanently clarifies the problem, but other people may experience a relapse. Both drugs can cause severe liver damage, sometimes causing death. Because propylthiouracil has caused many more cases of liver damage, it should generally be used only when it cannot tolerate methimazole. A small number of people who are allergic to these drugs can develop skin rashes, hives, fever or joint pain. They can also make you more susceptible to infection. Surgery (thyroidectomy). If you are pregnant or otherwise unable to tolerate antithyroid drugs and do not want or may not have radioactive iodine therapy, you may be a candidate for thyroid surgery, although this is an option in just a few cases. In a thyroidectomy, your doctor removes most of your thyroid gland. The risks of this surgery include damage to the vocal cords and parathyroid glands—four small glands located at the back of the thyroid gland that help control the level of calcium in the blood. In addition, you will need permanent treatment with levothyroxine (Levoxyl, Synthroid, others) to supply your body with normal amounts of thyroid hormone. If your parathyroid glands are also eliminated, you will need medications to keep your calcium levels in normal blood. Graves Ophthalmopathy If Graves' disease affects your eyes ( Graves' ophthalmopathy), you can manage mild signs and symptoms using artificial tears and lubricating gels and avoiding the wind and bright lights. If your symptoms are more severe, your doctor may recommend treatment with corticosteroids, such as prednisone, to reduce inflammation behind eyeballs. Two drugs — rituximab (Rituxan) and teprotumumab — are being used to treat Graves' ophthalmopathy, although there is still not much definitive evidence to prove that they are effective. Teprotumumab received rapid approval from the Food and Drug Administration on the basis of a small study. More study of both drugs is needed as treatment for Graves' ophthalmopathy. In some cases, a surgical procedure may be an option: Learn moreLifestyle and home remedies Once the treatment begins, the symptoms of hyperthyroidism should decrease and should start feeling much better. However, your doctor may recommend that you observe iodine in your diet because it can cause hyperthyroidism or make it worse. Kelp, dulse and other types of algae contain a lot of iodine. The cough syrup and multivitamins can also contain iodine. Gravel Disease If you have Graves' ophthalmopathy or dermopathy, the following suggestions can help your eyes or skin: Copy and support If you were diagnosed with hyperthyroidism, the most important thing is to receive the necessary medical care. After you and your doctor have decided a course of action, there are some things you can do that will help you cope with the condition and support your body during your healing process. Preparing your appointment You are likely to start by seeing your primary care doctor. However, in some cases, you may be immediately referred to a doctor who specializes in the hormone-secreting glands of the body (endocrynologist). If you have involvement in your eyes, you may also be referred to an eye doctor (oftalmologist). It's good to prepare for your date. Here are some information to help you prepare for your appointment, and to know what to expect from your doctor. What You Can DoPreparing a list of questions will help you to make the most of your time with your doctor. For hyperthyroidism, some basic questions to ask your doctor include: Do not hesitate to ask any other relevant questions you have. What to Expect from Your Doctor Your doctor will likely ask you several questions, including: RelatedAssociated Procedures Mayo Clinic NewsProducts & ServicesHyperthyroidism (Hyroid) Mayo Clinic does not support companies or products. Advertising revenues support our non-profit mission. Mayo Clinic Market Take a look at these best-sellers and special offers in Mayo Clinic books and newsletters. Any use of this site constitutes your agreement with the following Terms and Conditions and the Privacy Policy. A single copy of these materials can be reprinted for non-commercial personal use only. "Mayo", "Mayo Clinic", "MayoClinic.org", "Mayo Clinic Healthy Living", and the Mayo Clinic triple shield logo are trademarks of the Mayo Foundation for Medical Education and Research. This site complies with the information:

Ch37 - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology 6e Instructor Test Bank - StuDocu

Saunders Comprehensive Review for the NCLEX-RN® Examination - E-Book (Saunders Comprehensive Review by browsegrades.com - issuu

MCQ. Medical-surgical Nursing

NCLEX Review 3 Flashcards | Quizlet

Hypothyroidism and nursing care - American Nurse Today

ENDOFINALSTUDYGUIDE.docx - The nurse assesses the laboratory values for a patient with SIADH Which of the following are consistent with this diagnosis | Course Hero

Medical-Surgical Nursing: Med Surg Exam: All Question and Answers and the Rationale. by browsegrades.com - issuu

7 Hyperthyroidism (Grave's Disease) Nursing Care Plans

Hesi Exit Exam Review and Study Module Comprehensive with 265 Questions and Answers. Best for exam p by browsegrades.com - issuu

An incoherent female client with a history of hypothyroidism is brought to the | Course Hero

RN Comprehensive Predictor 2020 Form A2. Focussed Information You need to pass your examination. (1 by browsegrades.com - issuu

Hypothyroidism and nursing care - American Nurse Today

Nclex Practice: Questions, Answers and Rationale and The review information. Over 300 Questions and by browsegrades.com - issuu

Hypothyroidism and nursing care - American Nurse Today

AA RN Comprehensive Predictor 2019:Also ATI NCLEX Predictor. With 180 Q&A for nursing school personn by browsegrades.com - issuu
2 5 Nursing Management: Burns

Cardio-med surg Flashcards | Quizlet

SAUNDERS COMPREHENSIVE REVIEW FOR NCLEX THREE (Recovered). 1000 Questions and Answers. by browsegrades.com - issuu

NURSING NOTES: Reproduction Question and Answers With Explanations. Best Review Exam. by browsegrades.com - issuu

Hyperthyroidism: Diagnosis and Treatment - American Family Physician

Module 4 Thyroid/Para/Adrenal/Pituitary/AKI/CKD/Bioterrorism Flashcards | Quizlet

Endocrine System Disorders NCLEX-RN Practice Quiz (50 Questions)

NCLEX-RN Exam Cram: Practice Exam and Rationales | Quick Answers | Pearson IT Certification

Which prescribed medication should the nurse expect will have rapid effects on | Course Hero

Thyroid Tests | NIDDK

NCLEX-RN Practice Questions (Part 3) - NurseBuff

Hypothyroidism and nursing care - American Nurse Today

Bipolar Disorder Nursing Care Management Guide - Nurseslabs

Thyroidectomy | Thyroid Removal Surgery
![NCLEX Practice Questions: #1 Free NCLEX Test Bank [2021] - Nurseslabs NCLEX Practice Questions: #1 Free NCLEX Test Bank [2021] - Nurseslabs](https://nurseslabs.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/10/NCLEX-Practice-Questions-2021.jpg)
NCLEX Practice Questions: #1 Free NCLEX Test Bank [2021] - Nurseslabs

MCQ. Medical-surgical Nursing
Study Guide for Medical-Surgical Nursing: Assessment and Management of Clinical Problems

NCLEX Review 3 Flashcards | Quizlet

Hyperthyroidism: Diagnosis and Treatment - American Family Physician
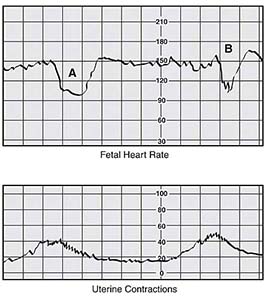
Practice for the NCLEX-RN: Practice Exam 3 and Rationales | Quick Check Answer Key | Pearson IT Certification

Eastern Nursing Research Society: 29th Annual Scientific Sessions Abstracts | Article | NursingCenter

Pin on Nurse love

ATI Comprehensive Practicing nurse(pn) test bank-NSG 4060

prep U 12 Head and Neck, Including Lymph Nodes and Vessels Flashcards | Quizlet
Posting Komentar untuk "which of the following would the nurse expect to find in a client with severe hyperthyroidism?"